Icosahedral symmetry
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Icosahedral group)
 Involutional symmetry Cs, (*) [ ] = |
 Cyclic symmetry Cnv, (*nn) [n] = |
 Dihedral symmetry Dnh, (*n22) [n,2] = |
|
| Polyhedral group, [n,3], (*n32) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Tetrahedral symmetry Td, (*332) [3,3] = |
 Octahedral symmetry Oh, (*432) [4,3] = |
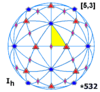 Icosahedral symmetry Ih, (*532) [5,3] = |
|
Icosahedral symmetry fundamental domains
A Soccer ball, a common example of a spherical truncated icosahedron, has full icosahedral symmetry.
The set of orientation-preserving symmetries forms a group referred to as A5 (the alternating group on 5 letters), and the full symmetry group (including reflections) is the product A5 × Z2. The latter group is also known as the Coxeter group H3, and is also represented by Coxeter notation, [5,3] and Coxeter diagram
Contents
As point group
Apart from the two infinite series of prismatic and antiprismatic symmetry, rotational icosahedral symmetry or chiral icosahedral symmetry of chiral objects and full icosahedral symmetry or achiral icosahedral symmetry are the discrete point symmetries (or equivalently, symmetries on the sphere) with the largest symmetry groups.Icosahedral symmetry is not compatible with translational symmetry, so there are no associated crystallographic point groups or space groups.
| Schö. | Coxeter | Orb. | Abstract structure |
Order | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | [5,3]+ | 532 | A5×2 | 60 | |
| Ih | [5,3] | *532 | A5 | 120 | |
The first presentation was given by William Rowan Hamilton in 1856, in his paper on icosian calculus.[1]
Note that other presentations are possible, for instance as an alternating group (for I).
Visualizations
| Schoe. (Orb.) |
Coxeter notation |
Elements | Mirror diagrams | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orthogonal | Stereographic projection | |||||
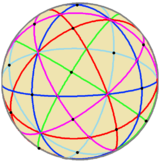
| Ih (*532) |
[5,3] |
Mirror lines: 15 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| I (532) |
[5,3]+ |
Gyration points: 125 203 302 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Group structure
 |
 |
| The edges of a spherical compound of five octahedra represent the 15 mirror planes. Each octahedron can represent 3 orthogonal mirror planes by its edges. | |
The group contains 5 versions of Th with 20 versions of D3 (10 axes, 2 per axis), and 6 versions of D5.
The full icosahedral group Ih has order 120. It has I as normal subgroup of index 2. The group Ih is isomorphic to I × Z2, or A5 × Z2, with the inversion in the center corresponding to element (identity,-1), where Z2 is written multiplicatively.
Ih acts on the compound of five cubes and the compound of five octahedra, but −1 acts as the identity (as cubes and octahedra are centrally symmetric). It acts on the compound of ten tetrahedra: I acts on the two chiral halves (compounds of five tetrahedra), and −1 interchanges the two halves. Notably, it does not act as S5, and these groups are not isomorphic; see below for details.
The group contains 10 versions of D3d and 6 versions of D5d (symmetries like antiprisms).
I is also isomorphic to PSL2(5), but Ih is not isomorphic to SL2(5).
Commonly confused groups
The following groups all have order 120, but are not isomorphic:- S5, the symmetric group on 5 elements
- Ih, the full icosahedral group (subject of this article, also known as H3)
- 2I, the binary icosahedral group
 is a normal subgroup of
is a normal subgroup of 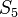
 is a factor of
is a factor of  , which is a direct product
, which is a direct product is a quotient group of
is a quotient group of 
 has an exceptional irreducible 3-dimensional representation (as the icosahedral rotation group), but
has an exceptional irreducible 3-dimensional representation (as the icosahedral rotation group), but 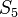 does not have an irreducible 3-dimensional representation,
corresponding to the full icosahedral group not being the symmetric
group.
does not have an irreducible 3-dimensional representation,
corresponding to the full icosahedral group not being the symmetric
group.These can also be related to linear groups over the finite field with five elements, which exhibit the subgroups and covering groups directly; none of these are the full icosahedral group:
 the projective special linear group, see here for a proof;
the projective special linear group, see here for a proof; the projective general linear group;
the projective general linear group; the special linear group.
the special linear group.
Conjugacy classes
| I | Ih |
|---|---|
|
|
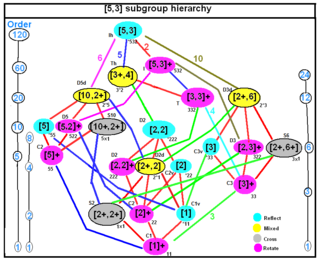
Subgroups of full icosahedral symmetry
Subgroup relations
Chiral subgroup relations
| Scho. | Coxeter | Orb. | H-M | Structure | Cyc. | Order | Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ih | [5,3] | *532 | 532/m | A5×2 | 120 | 1 | ||
| D2h | [2,2] | *222 | mmm | Dih2×Dih1=Dih13 | 8 | 15 | ||
| C5v | [5] | *55 | 5m | Dih5 | 10 | 12 | ||
| C3v | [3] | *33 | 3m | Dih3=S3 | 6 | 20 | ||
| C2v | [2] | *22 | mm2 | Dih2=Dih12 | 4 | 30 | ||
| Cs | [ ] | * | 2 or m | Dih1 | 2 | 60 | ||
| Th | [3+,4] | 3*2 | m3 | A4×2 | 24 | 5 | ||
| D5d | [2+,10] | 2*5 | 10m2 | Dih10=Z2×Dih5 | 20 | 6 | ||
| D3d | [2+,6] | 2*3 | 3m | Dih6=Z2×Dih3 | 12 | 10 | ||
| D1d = C2h | [2+,2] | 2* | 2/m | Dih2=Z2×Dih1 | 4 | 30 | ||
| S10 | [2+,10+] | 5× | 5 | Z10=Z2×Z5 | 10 | 12 | ||
| S6 | [2+,6+] | 3× | 3 | Z6=Z2×Z3 | 6 | 20 | ||
| S2 | [2+,2+] | × | 1 | Z2 | 2 | 60 | ||
| I | [5,3]+ | 532 | 532 | A5 | 60 | 2 | ||
| T | [3,3]+ | 332 | 332 | A4 | 12 | 10 | ||
| D5 | [2,5]+ | 225 | 225 | Dih5 | 10 | 12 | ||
| D3 | [2,3]+ | 223 | 223 | Dih3=S3 | 6 | 20 | ||
| D2 | [2,2]+ | 222 | 222 | Dih2=Z22 | 4 | 30 | ||
| C5 | [5]+ | 55 | 5 | Z5 | 5 | 24 | ||
| C3 | [3]+ | 33 | 3 | Z3=A3 | 3 | 40 | ||
| C2 | [2]+ | 22 | 2 | Z2 | 2 | 60 | ||
| C1 | [ ]+ | 11 | 1 | Z1 | 1 | 120 | ||
Note that the stabilizer of a vertex/edge/face/polyhedron and its opposite are equal, since
 is central.
is central.Vertex stabilizers
Stabilizers of an opposite pair of vertices can be interpreted as stabilizers of the axis they generate.- vertex stabilizers in I give cyclic groups C3
- vertex stabilizers in Ih give dihedral groups D3
- stabilizers of an opposite pair of vertices in I give dihedral groups D3
- stabilizers of an opposite pair of vertices in Ih give

Edge stabilizers
Stabilizers of an opposite pair of edges can be interpreted as stabilizers of the rectangle they generate.- edges stabilizers in I give cyclic groups Z2
- edges stabilizers in Ih give Klein four-groups

- stabilizers of a pair of edges in I give Klein four-groups
 ; there are 5 of these, given by rotation by 180° in 3 perpendicular axes.
; there are 5 of these, given by rotation by 180° in 3 perpendicular axes. - stabilizers of a pair of edges in Ih give
 ; there are 5 of these, given by reflections in 3 perpendicular axes.
; there are 5 of these, given by reflections in 3 perpendicular axes.
Face stabilizers
Stabilizers of an opposite pair of faces can be interpreted as stabilizers of the anti-prism they generate.- face stabilizers in I give cyclic groups C5
- face stabilizers in Ih give dihedral groups D5
- stabilizers of an opposite pair of faces in I give dihedral groups D5
- stabilizers of an opposite pair of faces in Ih give

Polyhedron stabilizers
For each of these, there are 5 conjugate copies, and the conjugation action gives a map, indeed an isomorphism, .
.- stabilizers of the inscribed tetrahedra in I are a copy of T
- stabilizers of the inscribed tetrahedra in Ih are a copy of Th
- stabilizers of the inscribed cubes (or opposite pair of tetrahedra, or octahedrons) in I are a copy of O
- stabilizers of the inscribed cubes (or opposite pair of tetrahedra, or octahedrons) in Ih are a copy of Oh
Fundamental domain
Fundamental domains for the icosahedral rotation group and the full icosahedral group are given by: Icosahedral rotation group I |
 Full icosahedral group Ih |
 Faces of disdyakis triacontahedron are the fundamental domain |
Solids with icosahedral symmetry
For more details on this topic, see Solids with icosahedral symmetry.
Chiral solids
| Class | Name | picture | Faces | Edges | Vertices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archimedean solid | snub dodecahedron |  |
92 | 150 | 60 |
| Catalan solid | pentagonal hexecontahedron |  |
60 | 50 | 92 |
Full icosahedral symmetry
| Platonic solids | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
{5,3} |
{3,5} |
|||
| Archimedean solids | ||||
3.10.10 |
 4.6.10 |
 5.6.6 |
 3.4.5.4 |
 3.5.3.5 |
| Catalan solids | ||||
 V3.10.10 |
 V4.6.10 |
 V5.6.6 |
V3.4.5.4 |
 V3.5.3.5 |
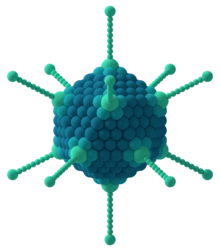
Other objects with icosahedral symmetry
Icosahedral capsid of an Adenovirus
| This section requires expansion. (January 2010) |
Liquid crystals with icosahedral symmetry
For the intermediate material phase called liquid crystals the existence of icosahedral symmetry was proposed by H. Kleinert and K. Maki[2] and its structure was first analyzed in detail in that paper. See the review article here. In aluminum, the icosahedral structure was discovered experimentally three years after this by Dan Shechtman, which earned him the Nobel Prize in 2011.Related geometries
Icosahedral symmetry is equivalently the projective special linear group PSL(2,5), and is the symmetry group of the modular curve X(5), and more generally PSL(2,p) is the symmetry group of the modular curve X(p). The modular curve X(5) is geometrically a dodecahedron with a cusp at the center of each polygonal face, which demonstrates the symmetry group.This geometry, and associated symmetry group, was studied by Felix Klein as the monodromy groups of a Belyi surface – a Riemann surface with a holomorphic map to the Riemann sphere, ramified only at 0, 1, and infinity (a Belyi function) – the cusps are the points lying over infinity, while the vertices and the centers of each edge lie over 0 and 1; the degree of the covering (number of sheets) equals 5.
This arose from his efforts to give a geometric setting for why icosahedral symmetry arose in the solution of the quintic equation, with the theory given in the famous (Klein 1888); a modern exposition is given in (Tóth 2002, Section 1.6, Additional Topic: Klein's Theory of the Icosahedron, p. 66).
Klein's investigations continued with his discovery of order 7 and order 11 symmetries in (Klein 1878/79b) and (Klein 1879) (and associated coverings of degree 7 and 11) and dessins d'enfants, the first yielding the Klein quartic, whose associated geometry has a tiling by 24 heptagons (with a cusp at the center of each).
Similar geometries occur for PSL(2,n) and more general groups for other modular curves.
More exotically, there are special connections between the groups PSL(2,5) (order 60), PSL(2,7) (order 168) and PSL(2,11) (order 660), which also admit geometric interpretations – PSL(2,5) is the symmetries of the icosahedron (genus 0), PSL(2,7) of the Klein quartic (genus 3), and PSL(2,11) the buckyball surface (genus 70). These groups form a "trinity" in the sense of Vladimir Arnold, which gives a framework for the various relationships; see trinities for details.
There is a close relationship to other Platonic solids.








No comments:
Post a Comment